
The genesis of the problem
What we are about to do here is to book an appointment but only if there are no other bookings already booked. The requirements as as fallow: Booking 1 (B1) ends at X time and Booking 2 (B2) can start at X time at the same time B2 ends at Y time and B3 can starts at Y time. The end time of B1 (B1.e) can be equal to start time of B2 (s.B2).
System description
Dates start and ends should be able to overlap. So for example it is allowed to book from 12:00 to 13:00 and from 13:00 to 14:00 and from 14:00 to 15:00. Note how two bookings can share the same starting and ending time.
Defining collision points
We can achieve that by detecting collision rows based on few collisions point. If the collision SELECT will return any data then its mean that there is at least one booking which don’t let us to create another booking.
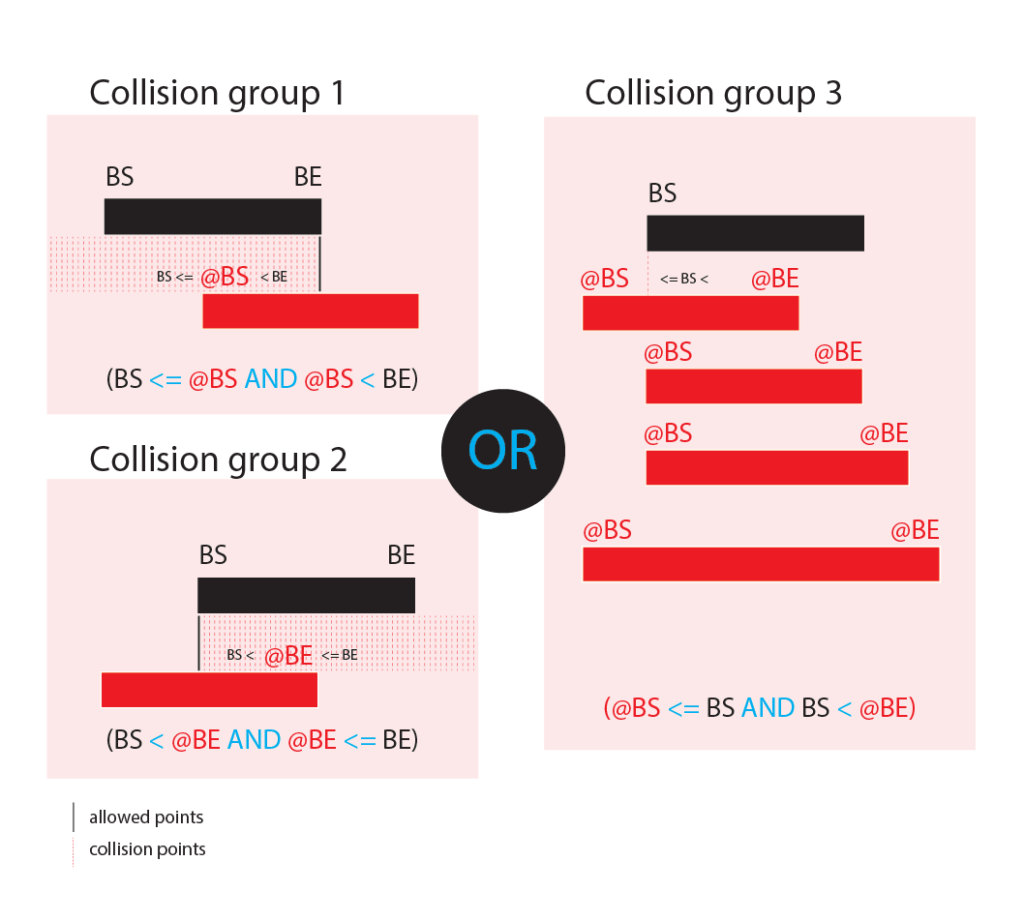
SELECT collision SQL query
SELECT id FROM appointments
WHERE
(starts_at <= @s AND @s < ends_at)
OR (starts_at < @e AND @e <= ends_at)
OR (@s <= starts_at AND starts_at < @e)
LIMIT 1 -- minimal query optimizationDatabase context
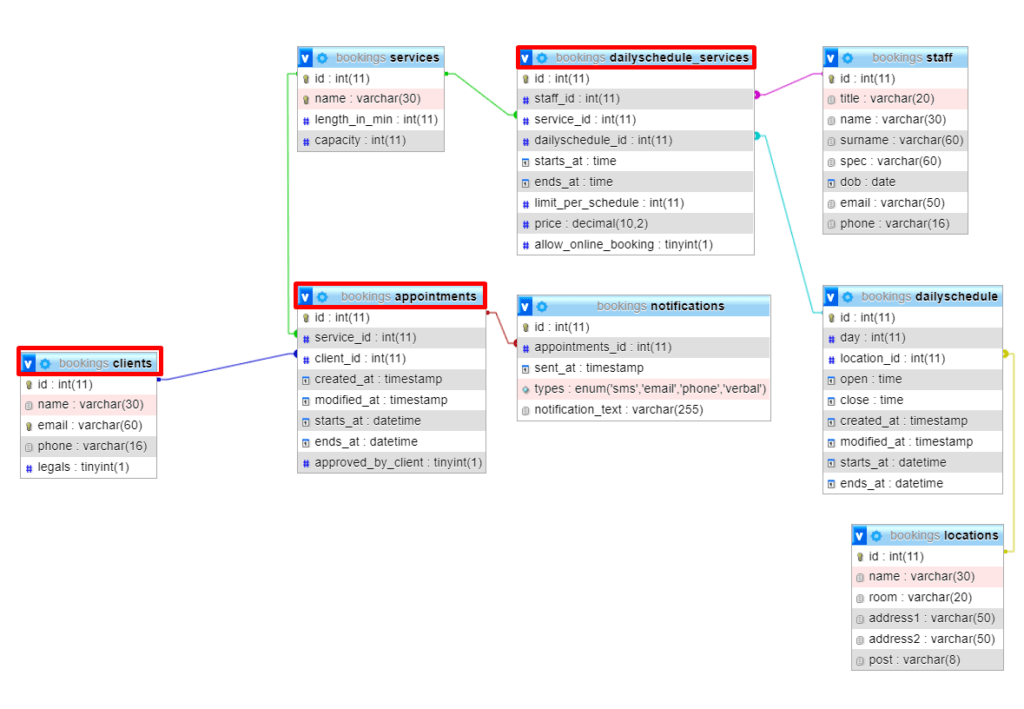
* Consider the fallowing database schema – GitHub (starting database create your own booking application)
Appointments table
+----+------------+-----------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+--------------------+
| id | service_id | client_id | created_at | modified_at | starts_at | ends_at | approved_by_client |
+----+------------+-----------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+--------------------+
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2021-07-15 16:57:59 | 2021-07-15 16:57:59 | 2021-07-10 11:00:00 | 2021-07-10 11:30:00 | 0 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 2021-07-15 16:57:59 | 2021-07-15 16:57:59 | 2021-07-10 12:00:00 | 2021-07-10 12:30:00 | 0 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 2021-07-15 16:57:59 | 2021-07-15 16:57:59 | 2021-07-10 13:00:00 | 2021-07-10 13:30:00 | 0 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 2021-07-15 16:57:59 | 2021-07-15 16:57:59 | 2021-07-10 13:30:00 | 2021-07-10 14:00:00 | 0 |
+----+------------+-----------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+--------------------+Condition INSERT query
INSERT SELECT (…) IF NOT EXISTS new booking starting at 2021-07-10 12:30:00 and ending at 2021-07-10 13:00:00.
SET @s := '2021-07-10 12:30:00';
SET @e := '2021-07-10 13:00:00';
INSERT INTO appointments
(client_id, service_id, starts_at, ends_at)
SELECT
(SELECT id FROM clients c WHERE c.email = 'some@email.com'),
(SELECT id FROM services s WHERE s.name = 'ANY'),
@s,
@e
WHERE
NOT EXISTS -- check if already booked or if there are any collisions with other booking. If there is collision found, collision booking is returned and no insert will be run
(
SELECT id FROM appointments
WHERE
(starts_at <= @s AND @s < ends_at)
OR (starts_at < @e AND @e <= ends_at)
OR (@s <= starts_at AND starts_at < @e)
LIMIT 1
)
AND EXISTS
(
SELECT 1 -- SOME OTHER CHECK
)
;Result:

Extending SQL query
The above example is a solution to a problem of finding collision and making insert if no collision are found. However we could simulate that we also have to check new booking against a admin defined schedule taking in to consideration a appointment type and staff. To achieve that we could populate a AND EXSIST section of the query.
Example table schema and demo data as your base to test below query GitHub
INSERT INTO appointments
(client_id, service_id, starts_at, ends_at)
SELECT
(SELECT id FROM clients c WHERE c.email = 'some@email.com'),
(SELECT id FROM services s WHERE s.name = 'ANY'),
@s,
@e
WHERE
EXISTS -- see if this timeslot is defined and available for booking in dailyschedule_services table
(
SELECT ss.id, sc.day FROM dailyschedule sc LEFT JOIN dailyschedule_services ss ON ss.dailyschedule_id = sc.id
WHERE
(service_id = (SELECT id FROM services s WHERE s.name = 'USG') OR service_id = (SELECT id FROM services s WHERE s.name = 'ANY'))
AND WEEKDAY(@s) + 1 = sc.day
AND @s >= sc.starts_at
AND TIME(@s) = ss.starts_at
AND TIME(@e) = ss.ends_at
)
AND
NOT EXISTS -- check if already booked or if there are any colisions with other booking. If there is colision found, colision booking is returned and no insert will be run
(
SELECT id FROM appointments
WHERE
(starts_at <= @s AND @s < ends_at)
OR (starts_at < @e AND @e <= ends_at)
OR (@s <= starts_at AND starts_at < @e)
LIMIT 1
)
AND
(1=1) -- CHECK FOR HOLIDAYS AND OFF DAYS
;
SELECT * FROM dailyschedule_services ss
LEFT JOIN dailyschedule s
ON ss.dailyschedule_id = s.id;
SELECT a.id, c.name, s.name, a.starts_at, a.ends_at
FROM appointments a
LEFT JOIN services s
ON a.service_id = s.id
LEFT JOIN clients c
ON a.client_id = c.id;Contribute
You have got to the end of this post on detecting collisions in SQL query. Let me know in the comments below or create a pull request at GitHub if you would want to improve any of the above schema or SQL query. Any optimization will be very welcome.
sell also:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/52740231/sql-find-free-slots-for-booking-system
and:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10132024/how-to-populate-a-table-with-a-range-of-dates
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/28388666/how-to-check-if-two-date-ranges-overlap-in-mysql/57237618#57237618
You have given very good examples. Thank you for sharing this SQL statement.
You are welcome, Ahmed. I am happy that you found it useful.
I have a project where end_at is undefined (NULL) which means it lasts until the end date is set. How to modify SQL to keep current functionality and check this condition. My project is about linking a person with a company (e.g. a person is an owner in a company or a co-owner and this state lasts from the start date but may end at an undefined time). start_at date is specified and end_at date is null
Sorry! Not enough information. You would have to explain the logic and constraints that you need to maintain for your application to run as expected. Perhaps stack overflow would be a better place to ask this question.